Roof load width rlw the other important consideration in determining timber lengths and sizes of your pergola is the size and weight of the roofing material the timber structure intends to hold up.
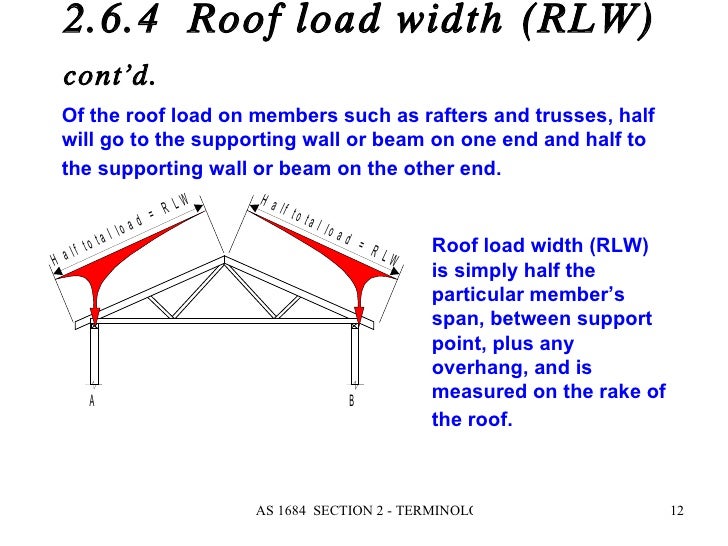
Roof load width definition.
D dead load l live load l r live roof load w wind load s snow load e earthquake load r rainwater load or ice water load t effect of material temperature h hydraulic loads from soil f hydraulic loads from fluids.
You can also use the wood beam calculator from the american wood council website to determine maximum rafter and joist lengths.
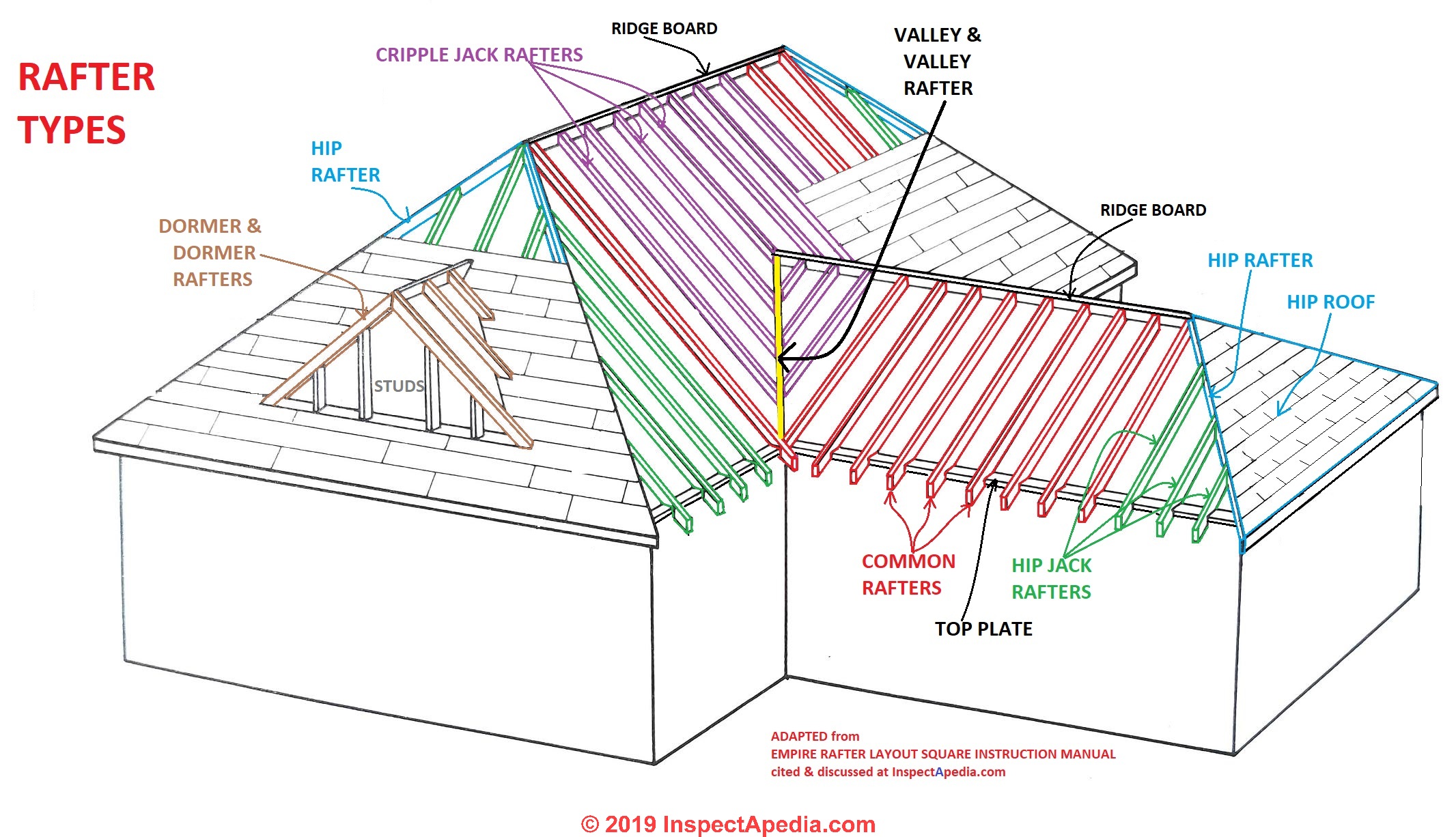
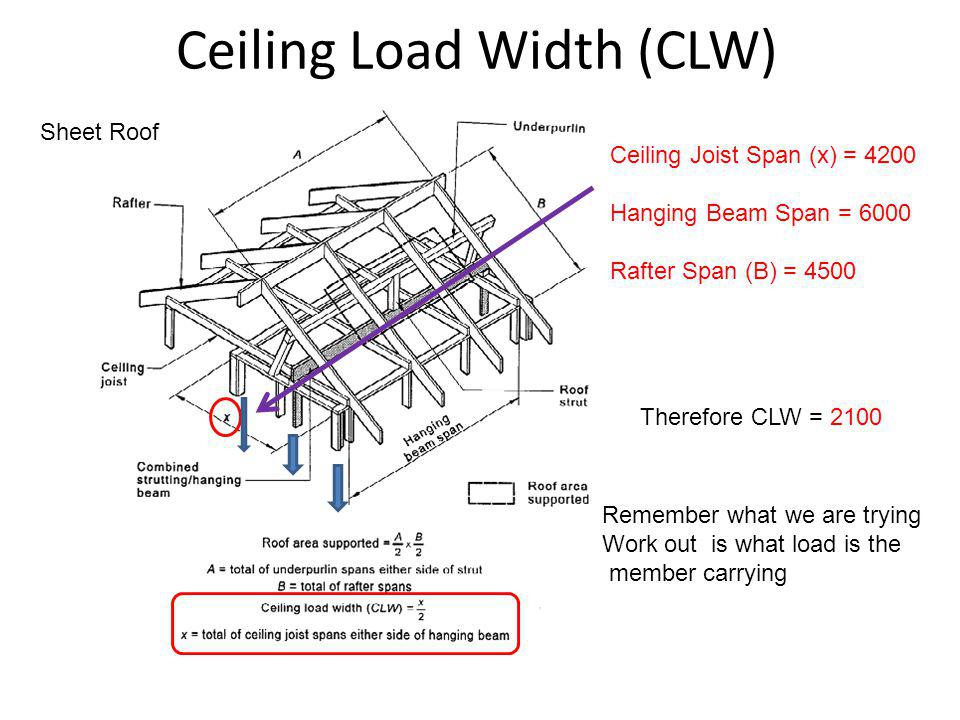
Tributary loading or tributary widthis the accumulation of loads that are directed toward a particular structural member.
If the load is 100 psf the load to the beam would be 12 ft x 100 psf 1200 plf.
Arch 331 note set 13 1 s2014abn 2.
Use the span tables below to determine allowable lengths of joists and rafters based on size and standard design loads.
This downward imposed load on the home is also known as the snow load.
The north zone design live load equates to 40 pounds per square foot the middle zone equates to 30 pounds per square foot and the south zone equates to 20 pounds per square foot.
2attic loads may be included in the floor live load but a 10 psf attic load is typically used only to size ceiling joists adequately for access purposes.
The left wall has 7 ft of tributary width and would receive a load of 700 plf.
The size of the roofing material is needed to calculate how much load the roof members and substructure need to support and therefore what size the underlying timber parts need to be.
The north zone middle zone and the south zone are identified on the roof load zone map above.
Load limits on the roof of a building.
However if the attic is intended for storage the attic live load or some portion should also be considered for the design of.
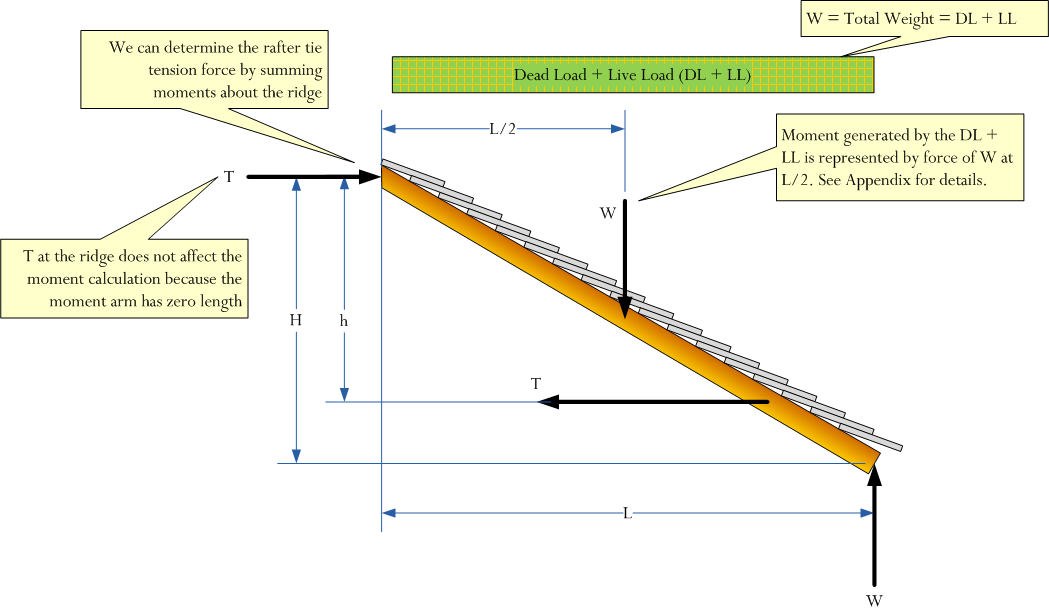
In order to stay intact and in place a roof must be able to resist loads both permanent and temporary that are pushing.
The exterior wall and the headers within will carry all loads from the mid point of the house between the supporting walls to the outside of the house including the roof overhang.
So each lineal foot of wall must carry the loads imposed by a 1 foot wide strip in that 14 ft region.